Projects Overview
Project Overview:
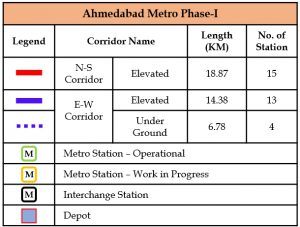
Ahmedabad Metro Project, Phase-I having two corridors i.e. North-South Corridor- APMC to Motera Stadium and East-West Corridor, Thaltej Gam to Vastral Gam was sanctioned by Government of India (GoI) in November, 2014.
The commercial operations of the Ahmedabad Metro Rail Project Phase-I began in March 2019 with 6.5 km viaduct and initial opening of Vastral Gam & Apparel Park stations, followed by Nirant Cross Road in April 2019, Amraiwadi in May 2019 and Vastral & Rabari Colony in March’21. Further, 32.1 km stretch became operational in October 2022. An additional 1.43 km stretch from Thaltej to Thaltej Gam opened for public in December 2024 , bringing the total span of Ahmedabad Metro Phase-I to 40.03 km with 31 stations.
The network details are as follows:
| Corridor | No. of Stations | Operational Stations | Route Length (km) | Operational Length (km) |
| East –West | 17 | 17 | 21.16 | 21.16 |
| North – South | 15 | 14 | 18.87 | 18.87 |
| Total | 32 | 31 | 40.03 | 40.03 |
Alignment Map
View on Interactive Map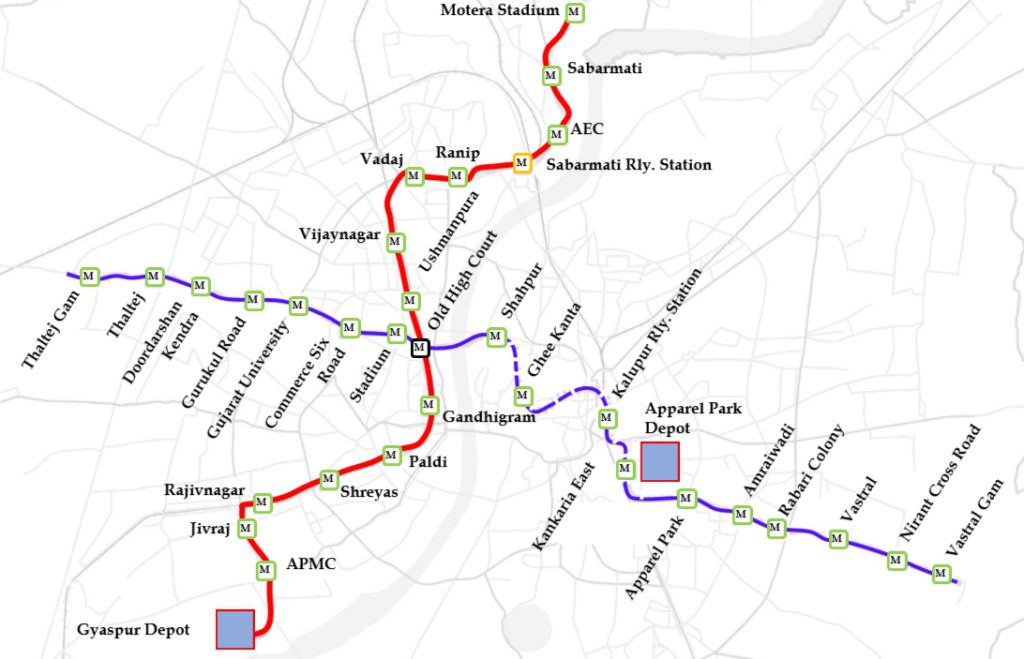
Project Overview:
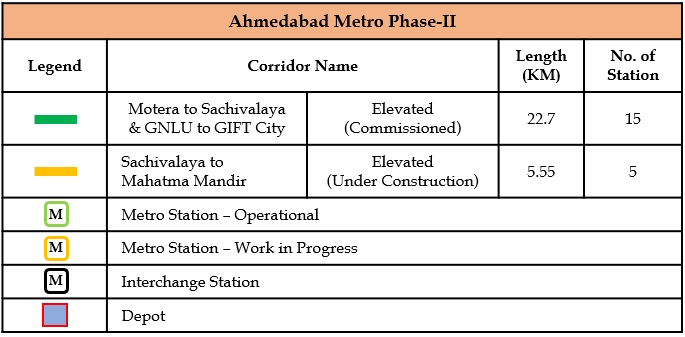
The Phase-II is an extension of the Phase-I that aims to connect the twin cities Ahmedabad and Gandhinagar. The network comprises of two corridors stretching 28.2km and having 22 stations. Out of 28.2 Km corridor, 20.8 Km and 8 stations from Motera to Mahatma Mandir and GNLU to GIFT City was inaugurated by Hon’ble Prime Minister on 16th September 2024. Additional 7 stations and 1.9 Km stretch from Sector-1 to Sachivalay metro station was opened to public on 27 April 2025.
The network details are as follows:
| Corridor | No. of Stations | Operational Stations | Route Length (km) | Operational Length (km) |
| Motera Stadium to Mahatma Mandir | 20 | 13 | 22.8 | 17.3 |
| GNLU to GIFT City | 2 | 2 | 5.4 | 5.4 |
| Total | 22 | 15 | 28.2 | 22.7 |
Alignment Map
View on Interactive Map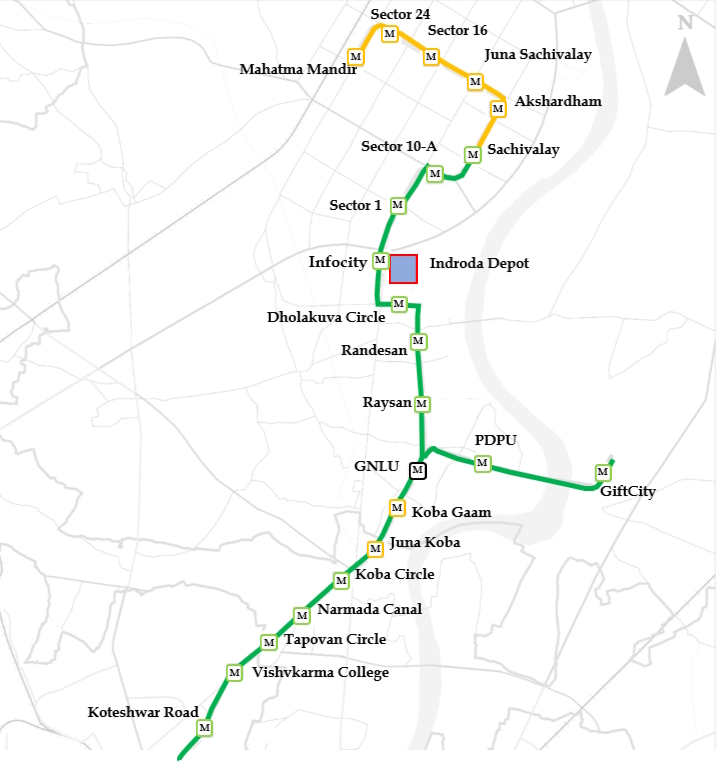
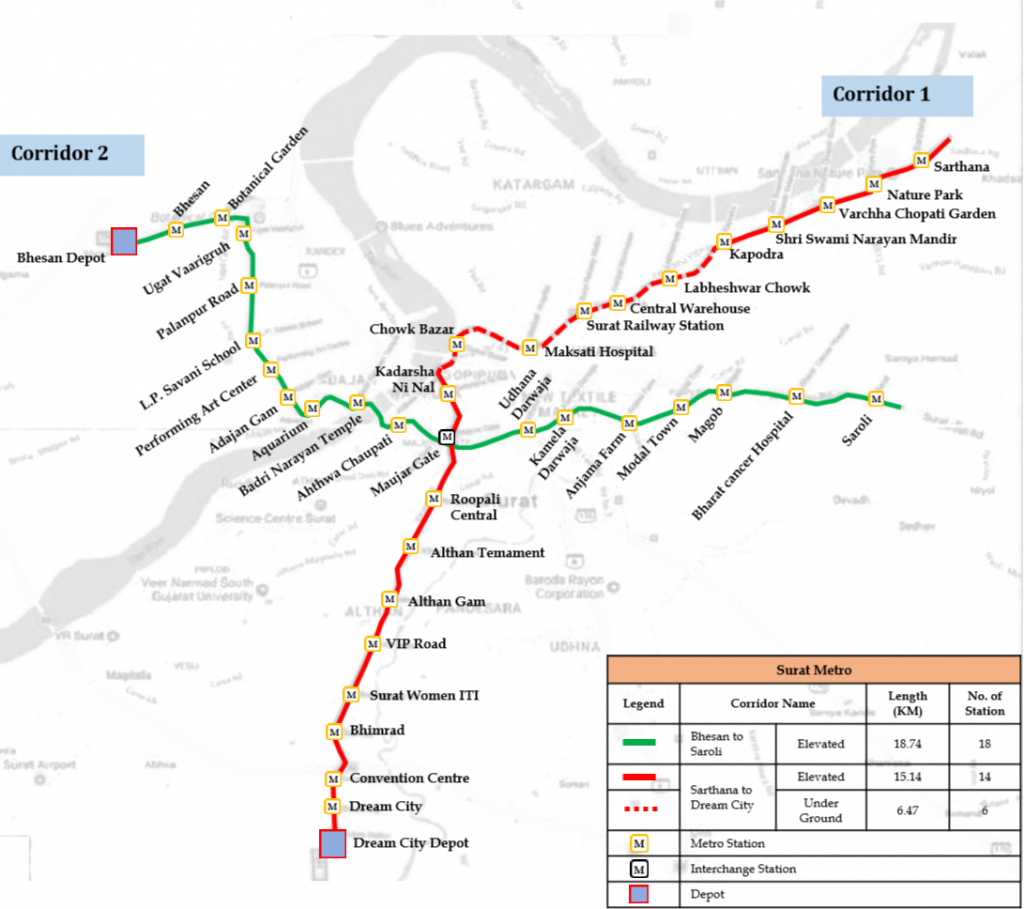
Project Overview:
Surat Metro Project comprises of two corridors : Corridor-1 -Sarthana to Dream city and Corridor 2- Bhesan to Saroli having 38 stations with a total length of 40.35 km of which 6.47 km is underground. The two (02) depots are located at Dream City and Bhesan. The civil construction work is under progress.
The network details are as follows:
| Corridor | Elevated | Underground | ||
| No. of Stations | Route Length (Km) | No. of Stations | Route Length (Km) | |
| Sarthana to Dream City | 14 | 15.14 | 6 | 6.47 |
| Bhesan to Saroli | 18 | 18.74 | – | – |
| Total | 28 | 33.88 | 6 | 6.47 |
Alignment Map
View on Interactive Map